- Population:
- 14,463,000
- Religion:
- Christianity
Benin's history is deeply connected to the powerful Kingdom of Dahomey, which thrived between the 17th and 19th centuries. It became a French colony in 1894 and was part of French West Africa until gaining independence in 1960. Post-independence, Benin went through a period of political instability and a Marxist-Leninist government before transitioning to a multi-party democracy in 1990. Today, it is a stable nation with a growing economy, focusing on agriculture and trade.
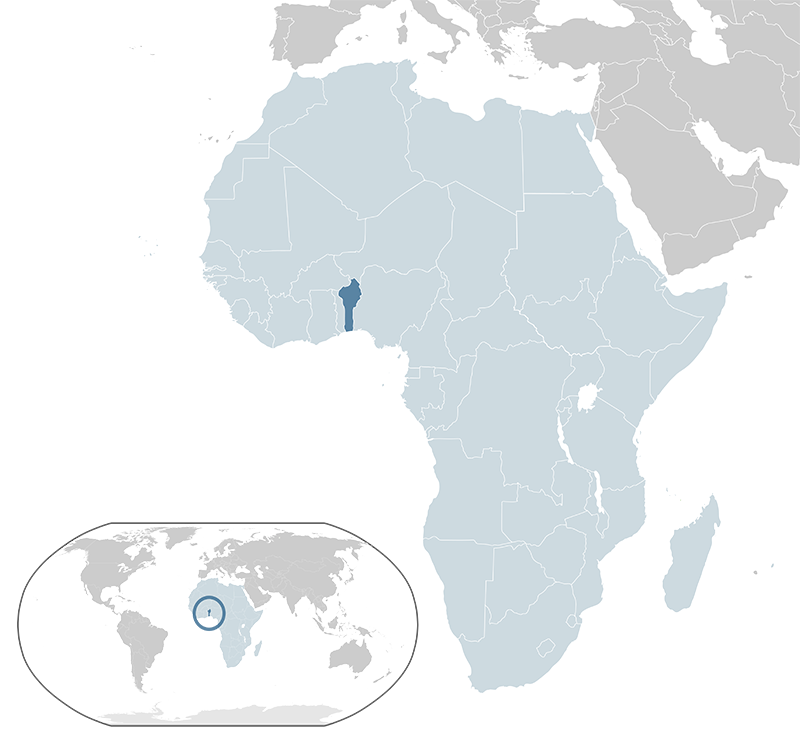
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. Covering an area of approximately 114,763 square kilometers, Benin has a population of about 12 million people. The capital city is Porto-Novo, but the seat of government is in Cotonou, the country's largest city and economic hub. The official language is French, with indigenous languages such as Fon and Yoruba also widely spoken. Benin operates as a presidential representative democratic republic. The economy is largely based on agriculture, with cotton being the main export commodity, and regional trade. Benin is known as the birthplace of the Vodun (Voodoo) religion and has a rich cultural heritage. The country is a member of the United Nations, the African Union, and the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).