- Population:
- 6,333,000
- Religion:
- Christianity
The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, was home to Bantu-speaking civilizations and the Kingdom of Kongo before European colonization. The French established control in the late 19th century, and the country gained independence in 1960. Post-independence, it experienced political instability, including periods of Marxist-Leninist rule and civil war in the 1990s. Today, Congo is rich in oil resources but faces economic and governance challenges.
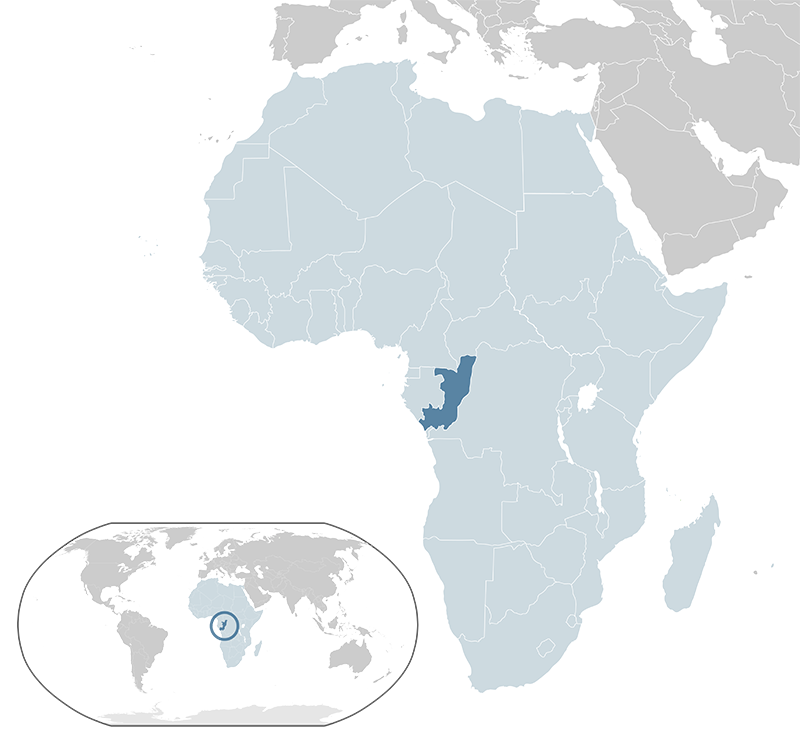
The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, is a country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Gabon to the west, Cameroon and the Central African Republic to the north, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the southwest. Covering an area of approximately 342,000 square kilometers, it has a population of about 6.2 million people as of 2023. The capital and largest city is Brazzaville. The official language is French, with national languages including Kituba and Lingala. The Republic of the Congo operates as a unitary semi-presidential republic. The economy is largely dependent on oil production, which accounts for a significant portion of its GDP, along with agriculture and forestry. The country is a member of the United Nations, the African Union, and the Economic Community of Central African States.