- Population:
- 1,169,000
- Religion:
- Islam
Djibouti's history includes early trade with Arabia and Africa and was home to the Afar and Issa peoples. It became a French colony in the 19th century and gained independence in 1977. Due to its strategic location at the entrance of the Red Sea, Djibouti hosts several foreign military bases and serves as a major shipping hub. It has remained relatively stable in a volatile region, relying on logistics and trade for its economy.
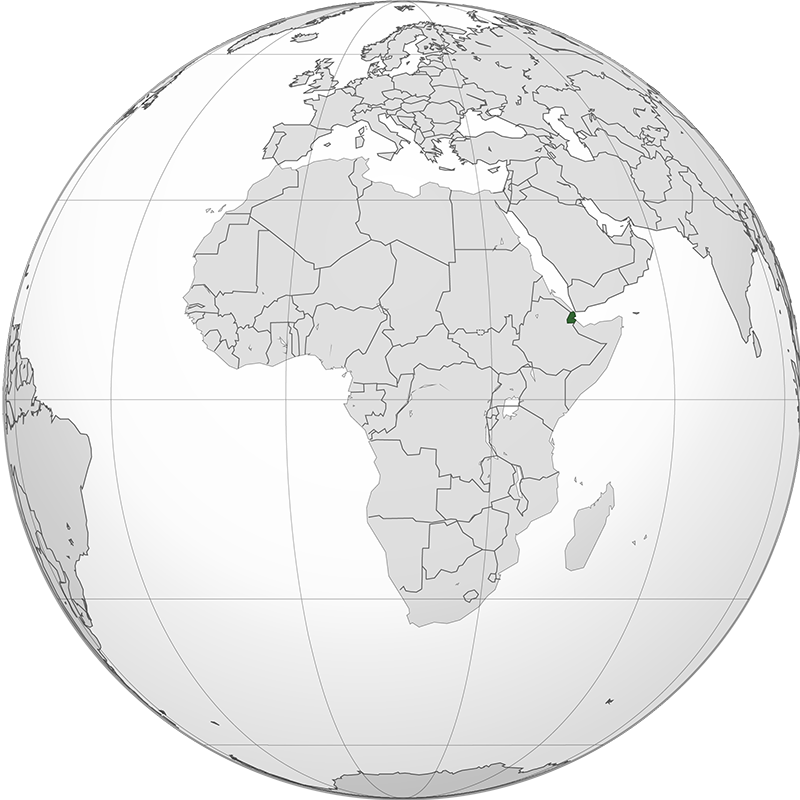
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea to the north, Ethiopia to the west and south, and Somalia to the southeast, with the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden lying to the east. Covering an area of approximately 23,200 square kilometers, Djibouti has a population of about 1 million people as of 2024. The capital and largest city is Djibouti City. The official languages are French and Arabic, with Somali and Afar also widely spoken. Djibouti operates as a unitary semi-presidential republic. The economy is primarily based on services, particularly as a strategic trade and logistics hub due to its location near one of the world's busiest shipping lanes. Djibouti hosts several foreign military bases and is a member of the United Nations, the African Union, and the Arab League.