- Population:
- 5,977,000
- Religion:
- Christianity
Denmark’s history traces back to the Vikings, who were influential across Europe during the Middle Ages. It later became a powerful kingdom, controlling Norway and parts of Sweden. After losing its empire, Denmark focused on democracy and social development. It remained neutral in World War I but was occupied by Nazi Germany in World War II. Today, it is a stable European democracy with a high quality of life and a strong welfare state.
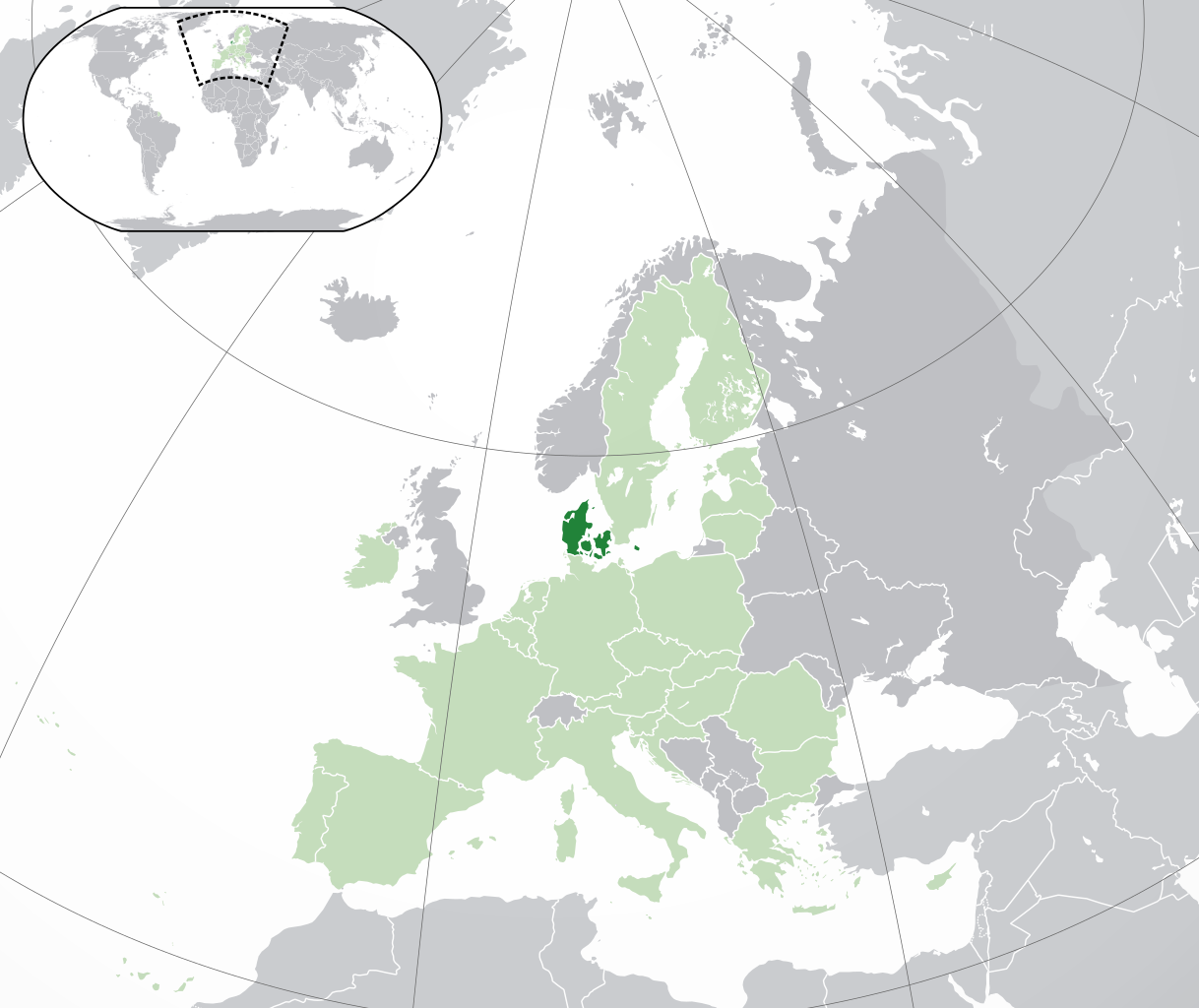
Denmark, officially the Kingdom of Denmark, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the southernmost of the Scandinavian nations, bordered to the south by Germany, and surrounded by the North Sea to the west, the Baltic Sea to the east, and Sweden to the northeast across the Øresund Strait. Denmark consists of the Jutland Peninsula and an archipelago of 443 named islands, covering a total area of approximately 42,933 square kilometers. As of 2024, the population is around 5.8 million people. The capital and largest city is Copenhagen. The official language is Danish. Denmark operates as a unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy. The economy is highly developed and diversified, with key sectors including manufacturing, services, and renewable energy. Denmark is known for its high standard of living, comprehensive welfare system, and commitment to environmental sustainability. It is a member of the European Union, the United Nations, NATO, and the Nordic Council.