- Population:
- 2,539,000
- Religion:
- Christianity
Gabon was originally inhabited by Bantu-speaking groups before becoming a French colony in the late 19th century. It gained independence in 1960 and has been politically stable compared to many of its African neighbors. Its economy relies on oil, which has brought wealth but also economic inequality. Gabon is known for its vast rainforests and conservation efforts, making it a key player in environmental preservation.
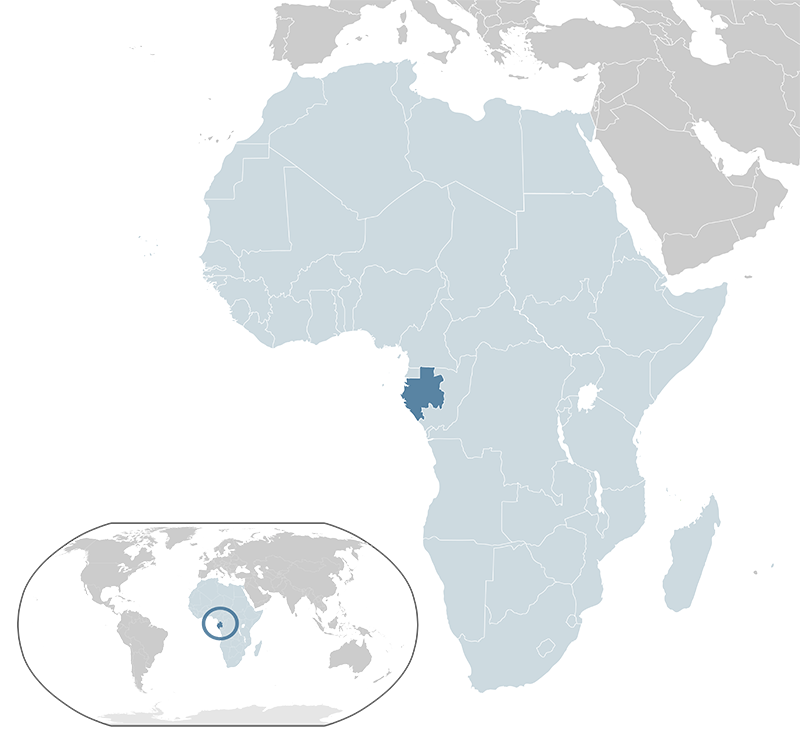
Gabon, officially the Gabonese Republic, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Covering an area of approximately 267,668 square kilometers, Gabon has a population of about 2.3 million people as of 2023. The capital and largest city is Libreville. The official language is French, with several indigenous languages also spoken. Gabon operates as a presidential republic. The economy is largely dependent on oil, which accounts for a significant portion of its GDP, along with mining and timber. Gabon is known for its rich biodiversity and extensive protected parkland, attracting ecotourism. It is a member of the United Nations, the African Union, and the Economic Community of Central African States.