- Population:
- 14,755,000
- Religion:
- Islam
Guinea was part of various West African empires before becoming a French colony in the late 19th century. It gained independence in 1958 under Sekou Touré, adopting a socialist system. Political instability followed, including military coups. Despite its rich mineral resources, particularly bauxite, Guinea remains one of the world's poorer nations, with ongoing governance challenges.
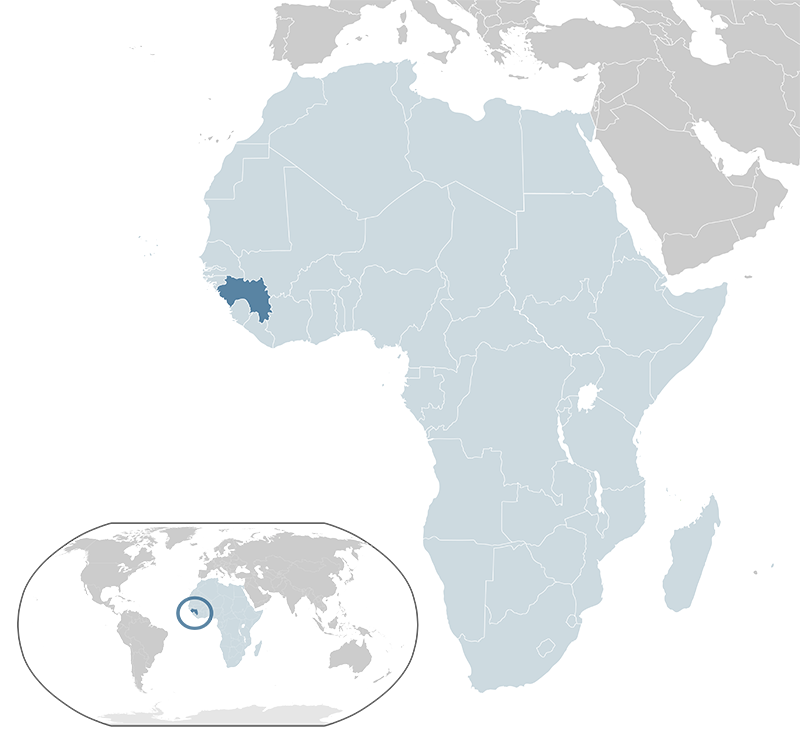
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Africa. It is bordered by Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, Liberia to the south, Sierra Leone to the southwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Covering an area of approximately 245,857 square kilometers, Guinea has a population of about 13.5 million people as of 2023. The capital and largest city is Conakry. The official language is French, with several indigenous languages also widely spoken. Guinea operates as a unitary presidential republic. The economy is rich in natural resources, particularly bauxite (used to produce aluminum), gold, and diamonds, but it remains one of the poorest countries due to infrastructure challenges and political instability. Guinea is a member of the United Nations, the African Union, and the Economic Community of West African States.